How a Data Trust Drives Effective Data Sharing, Privacy, and Analytics
How a Data Trust Drives Effective Data Sharing, Privacy, and Analytics
A growing number of government organizations are exploring data trusts as a foundation for information exchange. They recognize the value in formalizing data sharing relationships to enable participating agencies to capture previously unavailable information to achieve new insights.
At its core, a data trust is a legal framework for managing shared data. It enables participants to connect data sources and create a shared data repository. It also promotes collaboration through common rules for data access and security.
But a data trust is more than just a formal legal entity for creating a data repository. It actually delivers new value by encouraging the active sharing of data, strengthening data security and privacy, and promoting analytics that can result in greater visibility and improved citizen services.
Implemented well, a data trust can deliver:
1. A simplified and legal process for effective data sharing
Agreements for sharing data among organizations aren’t new. But traditional data agreements involve time-consuming negotiations between each agency. If a new agency wants to join the agreement, the process must be repeated, with different rules and technical details hammered out for each organization. The process is complex, costly, and potentially confusing.
A data trust simplifies and streamlines the process of achieving a data sharing agreement. It provides a common legal and technical framework that easily scales to new agencies, datasets, and use cases.
The legal document describes roles and responsibilities for all participants, both data contributors and data users. The approach ensures a standardized sharing process, with consistent requirements for all members. And by providing a scalable alternative to multiple point-to-point agreements, a legal trust reduces technical costs for onboarding and results in trusted relationships among participants.
2. Standards, data custody, and data protection for effective data privacy
In traditional sharing agreements, stakeholders often have concerns around data security and privacy. Different standards and processes negotiated for different participants can leave many worried about liability around exposure or misuse of data.
A data trust addresses these concerns through consistent standards for data custody and protection. It establishes common rules for data security and confidentiality: the specific data that will be shared, how it will be shared, which members will contribute to it, and which members will access it.
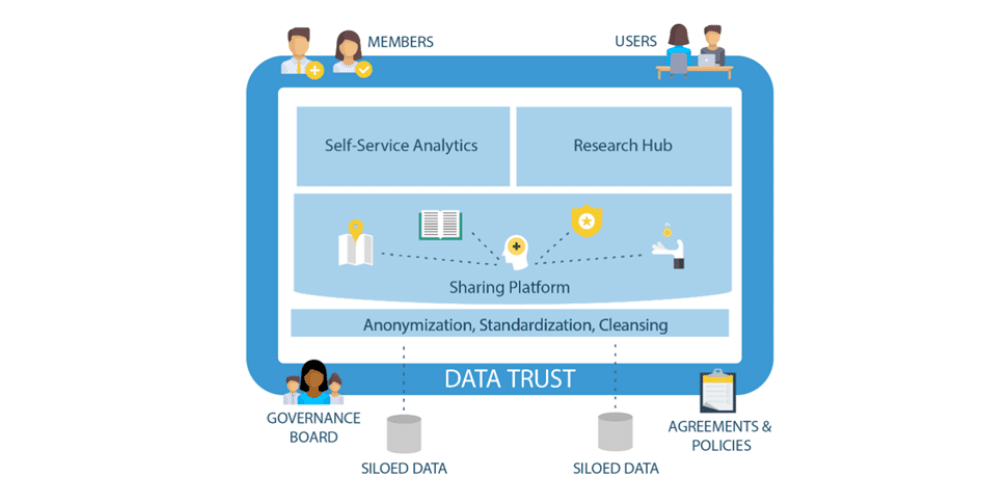
A data governance board is a key component of a data trust. Made up of select trust members, this decision-making body manages both the data trust and the information it collects, stores, and makes available for use. It makes sure all participants continue to adhere to the agreement, with technologies and processes in place to secure the data and protect personal identifiable information (PII).
3. Effective analytics for actionable insights and informed decisions
Agencies are awash in data. So, the goal of data sharing isn’t merely to generate new datasets. Rather, it’s to produce previously unavailable data feeds that can be analyzed to uncover emerging trends, create new understandings, and drive smart decisions.
In fact, a data trust is a highly effective way to optimize data analytics. Three essential components of a data trust contribute to this goal:
- Data sharing platform – A secure and scalable data repository ensures a single location for quality data.
- Research hub – An online portal built into the sharing platform allows approved researchers to access the data store.
- Self-service analytics – Prebuilt dashboards and tools enable members to consume and analyze data quickly and accurately.
In fact, a data trust can help advance participants on their journey to data analytics maturity. Organizations that have achieved analytics maturity efficiently apply information and insights to improve productivity, reimagine internal processes, and enhance services.
A growing number of organizations are benefiting from a data trust. For instance, the Commonwealth of Virginia has established the Commonwealth Data Trust to achieve a secure and legally compliant information sharing environment.
The initiative has delivered tangible results. As one example, Voyatek’s collaborated with the state to aggregate data from dozens of state agencies, career centers, and training institutes. Self-service dashboards give state leaders and policy-makers up-to-date insights into state workforce and employment trends. A public-facing dashboard, the Virginia Career Works Referral Portal, provides citizens with unemployment claims and payment data, census data, and labor market trends to help them advance their careers.
The need for organizations to share data will only grow. Through data trusts, they have a consistent, secure, and effective way to create a data repository that will help them gain greater visibility, make data-driven decisions, and deliver new services to citizens.

